Hip Arthritis
A progressive hip condition that can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and difficulty with everyday movement.
Hip arthritis is a common condition that may lead to pain, stiffness, and difficulty with movement. It occurs when the protective cartilage in the hip joint gradually wears away, causing the bones to rub together. This can result in inflammation, discomfort, and limitations in your day-to-day activities.
Recognising the signs of hip arthritis and understanding how it progresses is an important step toward managing your symptoms and exploring suitable treatment options. During your consultation, Dr Sam Martin will take the time to assess your condition and guide you through the available approaches, from non-surgical management to surgical intervention when appropriate.
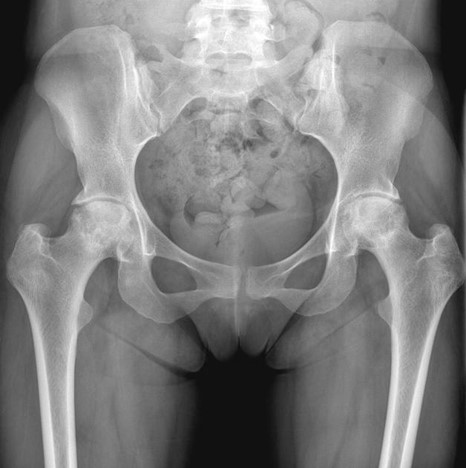
SYMPTOMS OF HIP ARTHRITIS

Hip arthritis can affect each person differently, but common symptoms often develop gradually and may worsen over time. Many people first notice a dull ache in the groin, thigh, or buttock that becomes more noticeable with activity. As the condition progresses, it may start to interfere with walking, bending, or even resting comfortably. The main symptoms can include:
- Persistent pain in the hip joint
- Stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity
- Swelling and tenderness around the hip
- Reduced range of motion
- A grinding sensation or sounds when moving the hip
- Difficulty walking or performing everyday activities
Recognising the early symptoms of hip arthritis can help you seek timely support. If you’re experiencing persistent hip discomfort or stiffness, Dr Martin can provide a thorough assessment to determine the cause and guide you toward appropriate treatment options.
TYPES OF HIP ARTHRITIS
There are several types of hip arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and post-traumatic arthritis, each with distinct characteristics and causes:
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, characterised by the gradual degeneration of cartilage in the hip joint. This wear-and-tear condition typically affects older adults but can also occur in younger individuals with a history of joint injuries or genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of OA:
Persistent hip pain, especially after activity Stiffness and limited range of motion Swelling and tenderness around the hip A grinding or clicking sensation during movement Increased pain in the morning or after periods of inactivity
Causes of OA include:
- Aging: Natural wear and tear of the joint over time
- Joint injuries: Previous fractures, ligament tears, or dislocations
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the hip joint
- Genetics: Family history of osteoarthritis
Treatment for OA:
- Non-Surgical: Medications (pain relievers, anti-inflammatories), physical therapy, weight management, and lifestyle modifications
- Surgical: Hip arthroscopy, osteotomy, partial hip replacement, and total hip replacement
Inflammatory Hip Arthritis refers to a group of conditions characterised by inflammation of the hip joint due to an autoimmune response. This type of arthritis can cause significant pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential joint damage.
Common Types of Inflammatory Arthritis:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. It often affects the lining of the joints (synovium) and may result in long-term joint damage if not managed. Common symptoms include swollen and tender joints, morning stiffness, fatigue, and sometimes fever or unintentional weight loss.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Related Arthritis: is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks healthy tissues, including the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. This arthritis often affects multiple joints, especially the hands, wrists, and knees, and can come and go in flares. Other symptoms of SLE may include fatigue, skin rashes, and organ involvement.
- Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and intense pain. It most commonly affects the big toe but can also involve other joints. Symptoms typically include severe pain, redness, warmth, and swelling in the affected joint. Gout attacks may come on suddenly and can be triggered by factors such as diet, dehydration, or certain medications.
Understanding the type of arthritis affecting your hip is an important step toward developing an effective treatment plan.
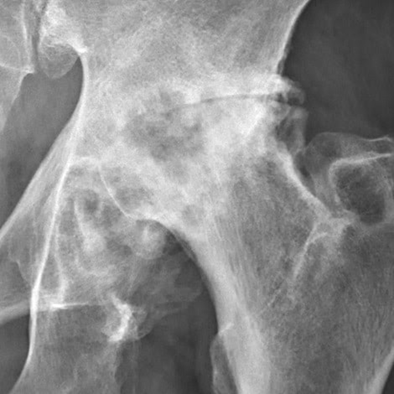
DIAGNOSING HIP ARTHRITIS

Dr Martin takes a thoughtful and thorough approach to diagnosing hip arthritis, ensuring that every aspect of your care is tailored to your specific symptoms and circumstances.
Your consultation will begin with a detailed discussion about your medical history, including any previous hip injuries or surgeries, as well as a careful review of your current symptoms. He will ask about the nature of your hip pain, how it started, how it affects your daily life, and any movements or activities that make it better or worse.
A physical examination will follow, during which Dr Martin will assess the strength, flexibility, and movement of your hip. This helps identify signs of joint stiffness, muscle weakness, or structural changes that may be contributing to your pain.
To gain a clearer understanding of your hip joint and the surrounding structures, Dr Martin may recommend further investigations such as X-rays, CT scans, or other specialised tests to assist in accurately identifying the source of your symptoms.
By combining these assessments with clinical expertise, Dr Martin will work with you to form a clear diagnosis and outline the most appropriate treatment options for your situation.
TREATING HIP ARTHRITIS
While there is no cure for hip arthritis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroid injections.
- Physiotherapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around the hip and improve flexibility.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, low-impact activities, and using supportive devices like braces or orthotics.
Surgical Treatments:
- Hip Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to clean out the joint or repair damage.
- Osteotomy: Realigning bones to relieve pressure on the hip joint.
- Partial Hip Replacement: Replacing only the damaged part of the hip.
- Total Hip Replacement: Replacing the entire hip joint with an artificial implant.

